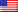
Huawei is adapting its in-vehicle infotainment system for the Aito M9 SUV to meet the demands of international markets, as revealed by recent leaked screenshots. The changes indicate a deliberate effort to localize navigation, driver-assistance features, and app support for non-Chinese users. This move is critical because automotive software must comply with regional regulations, mapping data standards, and user expectations to succeed abroad.
Navigation and Mapping Adjustments
The most visible change is the replacement of Chinese map services with international providers. The infotainment now displays English-language labeling and routing formats common in North America and Europe. This isn’t merely cosmetic: it signifies a complete overhaul of the vehicle’s navigation stack to align with licensing requirements, search databases, and regional data accuracy outside of China.
ADS Adaptation for International Roads
Huawei’s Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADS) has been refined for driving conditions outside China. While the core layout remains similar, lane markings, speed limit indicators, and environmental prompts have been adjusted to comply with North American and European standards. This suggests that the ADS software is undergoing rigorous alignment with international regulatory and operational benchmarks, ensuring safe and legal operation in diverse environments.
Globalized User Interface
System menus, settings pages, voice-assistant onboarding, and media controls have been translated into English, with iconography and formatting adjusted to ensure usability for international drivers. The overall structure follows common overseas UI patterns, avoiding reliance on Chinese-language conventions that would hinder adoption. Crucially, domestic Chinese apps have been swapped out for globally recognized alternatives in music and video streaming.
Vehicle Specifications: Aito M9 Overview
The Aito M9 is a full-size SUV measuring 5230 mm in length, 1999 mm in width, and 1800 mm in height, with a 3110 mm wheelbase. It is available in five- or six-seat configurations and comes in both pure electric (EV) and range-extended electric (EREV) versions. The EV variant produces 390 kW (523 hp) and 673 Nm of torque, offering a CLTC range of 605 km and a 0–100 km/h acceleration time of 4.7 seconds. The EREV version combines a 1.5-liter turbocharged petrol engine with dual electric motors, delivering 365 kW (489 hp) and 675 Nm of torque, and a combined CLTC range of up to 1,417 km. Both versions feature all-wheel drive, 21-inch wheels, and four LiDAR units for Huawei’s ADS. Curb weights range from approximately 2,655 kg for the EV to 2,690 kg for the EREV.
The screenshots demonstrate that Huawei is not simply translating software but rebuilding it to function seamlessly in international contexts. This level of adaptation is essential before any China-developed vehicle can successfully enter overseas markets.
The leaked images confirm that Huawei is aggressively preparing its infotainment system for global deployment, but an official launch timeline remains undisclosed. The extensive localization efforts highlight the complex logistical and technical hurdles of exporting automotive software, where compliance and usability are paramount.